Understanding Quantum Entanglement: A Complete Guide
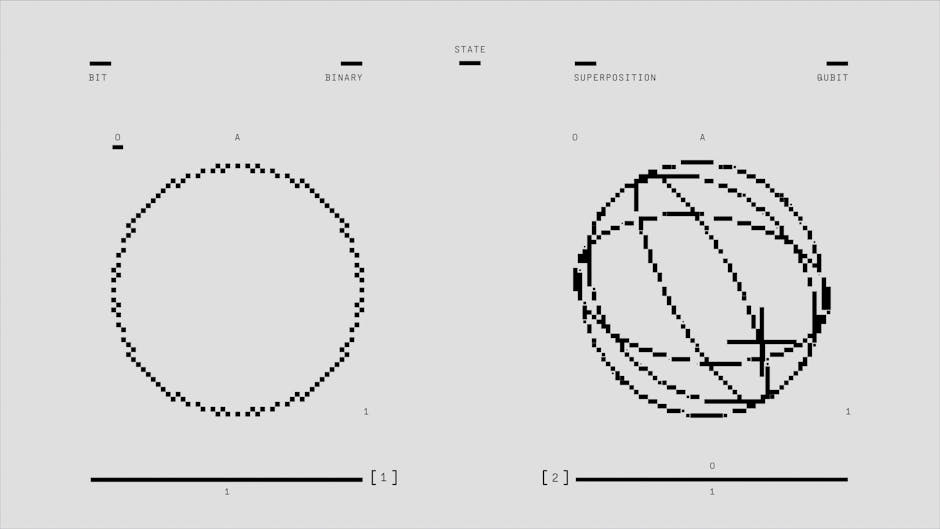
Quantum entanglement is one of the most intriguing phenomena in modern physics. It describes a situation where two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one immediately influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance separating them. This phenomenon challenges our classical understanding of quantum mechanics and has significant implications for advancements in quantum computing, cryptography, and secure communications.
Historically, scientists like Albert Einstein referred to entanglement as "spooky action at a distance," expressing initial skepticism about its implications. However, numerous experiments, such as those conducted by Bell's theorem tests, have confirmed the reality of entanglement. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for developing next-generation technologies that leverage quantum properties for unprecedented processing power and security.
In practical terms, quantum entanglement applications are already emerging. For example, in quantum teleportation, information is transferred instantaneously between entangled particles, paving the way for ultra-secure quantum cryptography. Researchers are also exploring entanglement-based quantum internet networks to enable instantaneous and unhackable communication over long distances.
To learn more about this mesmerizing phenomenon, check out our detailed guide on entanglement and its role in the future of physics and technology. Whether you're a student, researcher, or enthusiast, understanding entanglement can open up new perspectives on the universe's fundamental workings.
For visual learners, imagine two entangled particles as two identical twins separated by a vast distance, yet somehow sharing an unbreakable bond. When one twin makes a decision or experiences a change, it instantly reflects in the other, no matter how far apart they are.

