Quantum Physics Explained For Beginners
Introduction to Quantum Physics
Quantum physics is a fundamental branch of science that explores the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales—atoms and subatomic particles. For those new to the subject, understanding quantum physics might seem daunting, but grasping some core concepts can open doors to the fascinating world of quantum mechanics.
The Basics of Quantum Mechanics
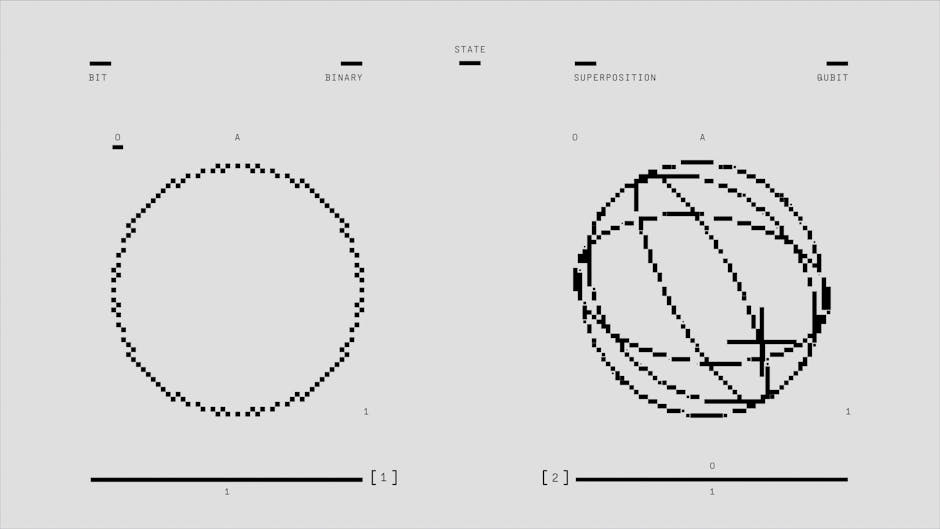
At its heart, quantum mechanics describes how particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously—known as superposition—and how observations can affect the state of a system. Unlike classical physics, which describes macroscopic objects, quantum physics deals with probabilities rather than certainties.
Key Principles of Quantum Physics
- Wave-Particle Duality: Particles like electrons and photons can behave both as particles and waves, depending on how they are observed.
- Quantization: Energy levels are discrete rather than continuous, meaning particles can only inhabit specific energy states.
- Uncertainty Principle: The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that certain pairs of properties, like position and momentum, cannot be precisely measured simultaneously.
Why Quantum Physics Matters
Understanding quantum physics has led to technological advances such as quantum computing, secure communication, and the development of new materials. Its principles challenge our classical intuition, prompting ongoing research into the fundamental nature of reality.
Further Resources
If you're interested in exploring further, check out our detailed articles on quantum entanglement and quantum superposition.
