Understanding Quantum Computing: An Overview of Superposition
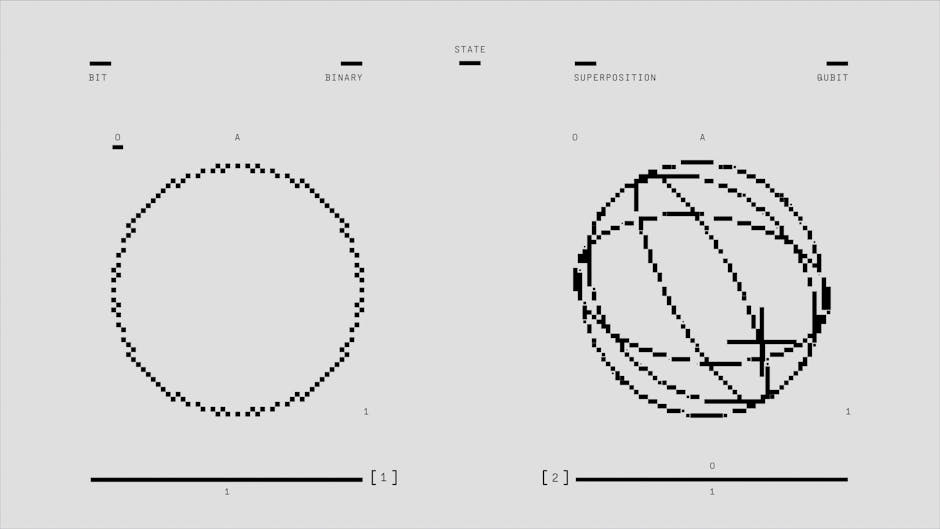
Quantum computing is an emerging field that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations more efficiently than traditional computers. At the heart of this technology lies the fascinating concept of superposition, which allows quantum bits, or qubits, to exist in multiple states simultaneously. This unique property enables quantum computers to process a vast number of possibilities at once, making certain calculations exponentially faster.
Unlike classical bits that are either 0 or 1, qubits can be in a combination of both states thanks to superposition. For example, a qubit in superposition can simultaneously represent 0, 1, and all intermediate states, granting quantum systems their powerful parallel processing capabilities. This enables tasks such as factoring large numbers and simulating molecular structures to be performed more efficiently.
Understanding superposition is crucial to grasping how quantum computing can revolutionize technology. To learn more about how superposition works within quantum systems, visit the superposition section of our overview. As research continues, the potential applications of quantum computing are expanding, promising breakthroughs in fields ranging from cryptography to material science.
