Understanding Quantum Superposition: A Beginner's Guide to Quantum Physics
Introduction to Quantum Superposition
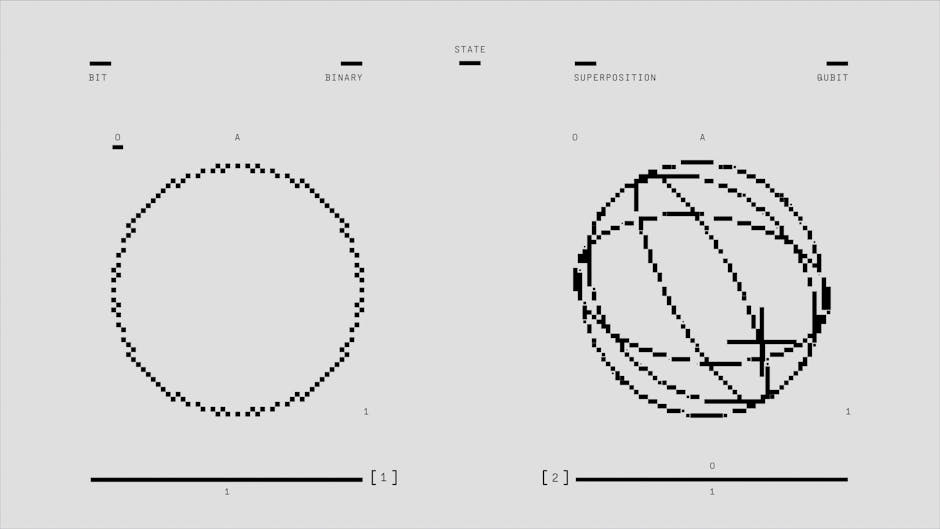
Quantum superposition is a fundamental principle of quantum physics that describes how particles can exist in multiple states at once until they are observed or measured. This intriguing idea challenges our classical understanding of nature and has profound implications for the development of quantum technologies.
What Is Quantum Superposition?
At its core, quantum physics explains phenomena that cannot be explained by classical physics. Superposition refers to the ability of a quantum system to be in a combination of states simultaneously. For example, a quantum particle such as an electron can exist in multiple positions or spin states at the same time.
Implications and Applications
This principle underpins many exciting developments in science and technology, including quantum computing and quantum cryptography. By harnessing superposition, quantum computers can process complex computations much faster than classical computers.
Experiments Demonstrating Superposition
Experiments like the famous double-slit experiment demonstrate superposition by showing interference patterns, which only occur when particles are in multiple states simultaneously. These experiments continue to deepen our understanding of the quantum world.
Conclusion
Quantum superposition remains one of the most mind-bending and exciting concepts in physics. As research advances, our grasp of this phenomenon will likely lead to revolutionary technological innovations and a deeper comprehension of the universe.
